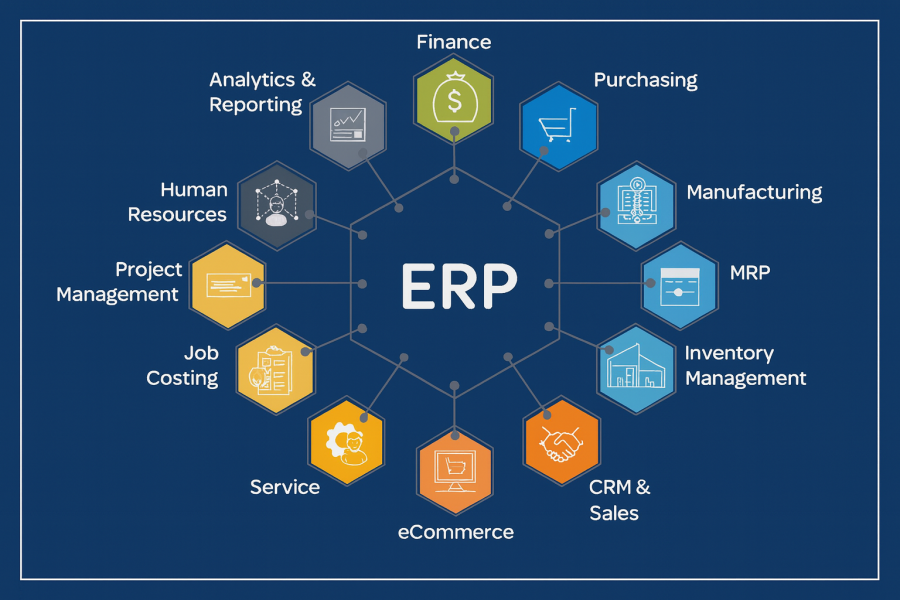
How ERP Centralizes Business Operations
Managing a business today means handling a wide network of activities — sales, finance, HR, supply chain, procurement, and customer service. When each department works on separate tools or isolated spreadsheets, inefficiencies are bound to arise. Miscommunication increases, data gets duplicated, and everyday operations become slower than they should be.
This is exactly where ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) transforms the picture. An ERP system unifies all business functions on a single digital platform so teams no longer operate in silos. It becomes the central system of record, improving accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration across the entire organization.
What Does Centralization Really Mean?
Centralization refers to consolidating all business information and processes into one system. Imagine sales, finance, HR, and warehouse teams working in real time on the same dataset. No repeated data entry. No conflicting spreadsheets. No guesswork.
This unified approach not only saves time — it strengthens communication, ensures consistency, and provides complete transparency across the company.
How ERP Centralizes Business Operations
1. One Unified Database
The foundation of ERP is a single, centralized database. Whether it’s customer data, invoices, purchase orders, or stock levels, everything lives in one place. For example:
When a sales order is created, inventory adjusts instantly.
Finance can raise an invoice without waiting for manual updates.
Management can access real-time dashboards anytime.
With one version of truth, errors, duplicates, and outdated information disappear.
2. Integrated Modules for Every Department
ERP systems include interconnected modules designed for various business functions:
Finance: Billing, accounting, taxes, and expense management
Sales & CRM: Leads, quotations, and customer lifecycle
Inventory & Supply Chain: Stock, warehouses, procurement, and logistics
HR & Payroll: Employee data, attendance, leave, and salaries
Manufacturing / Projects: Production planning, BOMs, timelines, and execution
Since all modules are linked, one update instantly reflects everywhere.
Example: A purchase order automatically updates inventory, payables, and budgets simultaneously.
3. Smarter, Automated Workflows
Without ERP, approvals often get buried in emails. ERP automates end-to-end workflows:
Leave requests move automatically from employee → manager → HR → payroll
Purchase approvals flow from request → approval → vendor → inventory
This removes manual bottlenecks, speeds up processes, and increases accountability.
4. Real-Time, Cross-Department Collaboration
Centralization encourages seamless communication among teams.
Sales checks live stock levels before confirming orders.
HR and finance collaborate on payroll without exchanging files.
Managers access consolidated reports instead of waiting for weekly updates.
Everyone stays aligned, informed, and connected.
5. Data-Driven, Real-Time Decision Making
ERP eliminates outdated reports and provides instant insights.
Examples: A retailer can track fast-moving items and restock immediately.
A manufacturer can monitor downtime trends and schedule maintenance proactively.
Leaders can analyze live performance metrics and make faster strategic decisions.
Why Centralization Matters
When operations aren’t centralized, businesses struggle with:
Duplicate records and human errors
Wasted time reconciling multiple systems
Poor customer experience due to communication gaps
Higher operational costs and slower response times
With ERP, every function works together like a synchronized system. Leaders focus on growth—not correcting mistakes or chasing information.
A Real-World Example
Without ERP:
Sales creates an order without checking stock.
Warehouse realizes the product is unavailable.
Finance prepares the invoice manually and makes mistakes.
Customer service receives complaints about delays.
With ERP:
Sales enters the order and stock adjusts instantly.
Warehouse is alerted in real time.
Finance generates an accurate invoice automatically.
Customer support has full visibility of order status.
This is exactly where ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) transforms the picture. An ERP system unifies all business functions on a single digital platform so teams no longer operate in silos. It becomes the central system of record, improving accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration across the entire organization.
What Does Centralization Really Mean?
Centralization refers to consolidating all business information and processes into one system. Imagine sales, finance, HR, and warehouse teams working in real time on the same dataset. No repeated data entry. No conflicting spreadsheets. No guesswork.
This unified approach not only saves time — it strengthens communication, ensures consistency, and provides complete transparency across the company.
How ERP Centralizes Business Operations
1. One Unified Database
The foundation of ERP is a single, centralized database. Whether it’s customer data, invoices, purchase orders, or stock levels, everything lives in one place. For example:
When a sales order is created, inventory adjusts instantly.
Finance can raise an invoice without waiting for manual updates.
Management can access real-time dashboards anytime.
With one version of truth, errors, duplicates, and outdated information disappear.
2. Integrated Modules for Every Department
ERP systems include interconnected modules designed for various business functions:
Finance: Billing, accounting, taxes, and expense management
Sales & CRM: Leads, quotations, and customer lifecycle
Inventory & Supply Chain: Stock, warehouses, procurement, and logistics
HR & Payroll: Employee data, attendance, leave, and salaries
Manufacturing / Projects: Production planning, BOMs, timelines, and execution
Since all modules are linked, one update instantly reflects everywhere.
Example: A purchase order automatically updates inventory, payables, and budgets simultaneously.
3. Smarter, Automated Workflows
Without ERP, approvals often get buried in emails. ERP automates end-to-end workflows:
Leave requests move automatically from employee → manager → HR → payroll
Purchase approvals flow from request → approval → vendor → inventory
This removes manual bottlenecks, speeds up processes, and increases accountability.
4. Real-Time, Cross-Department Collaboration
Centralization encourages seamless communication among teams.
Sales checks live stock levels before confirming orders.
HR and finance collaborate on payroll without exchanging files.
Managers access consolidated reports instead of waiting for weekly updates.
Everyone stays aligned, informed, and connected.
5. Data-Driven, Real-Time Decision Making
ERP eliminates outdated reports and provides instant insights.
Examples: A retailer can track fast-moving items and restock immediately.
A manufacturer can monitor downtime trends and schedule maintenance proactively.
Leaders can analyze live performance metrics and make faster strategic decisions.
Why Centralization Matters
When operations aren’t centralized, businesses struggle with:
Duplicate records and human errors
Wasted time reconciling multiple systems
Poor customer experience due to communication gaps
Higher operational costs and slower response times
With ERP, every function works together like a synchronized system. Leaders focus on growth—not correcting mistakes or chasing information.
A Real-World Example
Without ERP:
Sales creates an order without checking stock.
Warehouse realizes the product is unavailable.
Finance prepares the invoice manually and makes mistakes.
Customer service receives complaints about delays.
With ERP:
Sales enters the order and stock adjusts instantly.
Warehouse is alerted in real time.
Finance generates an accurate invoice automatically.
Customer support has full visibility of order status.